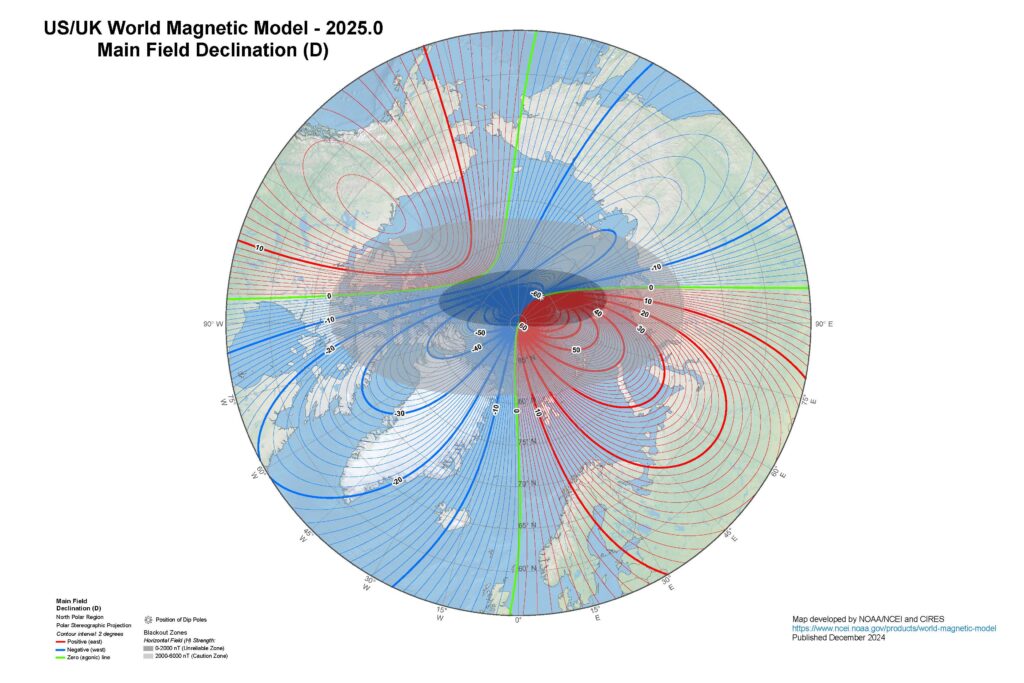
The latest version of the World Magnetic Model (WMM), one of the key tools developed to model changes in Earth’s magnetic field, has been released. The WMM is a spherical harmonic model of the Earth’s main magnetic field and its slow temporal variation. WMM is the key to global navigation, ensuring that technical systems that rely on the Earth’s magnetic field operate correctly.
World Magnetic Model 2025 (WMM2025) provides more accurate navigation data for all military and civilian aircraft, ships, submarines, and GPS units. Two versions of the model will be released this year. In addition to WMM2025, this release includes the first World Magnetic Model High Resolution (WMMHR2025), which improves spatial resolution at the equator by approximately 300 kilometers compared to the standard spatial resolution of 3,300 kilometers at the equator. . The higher the resolution, the better the orientation accuracy. We recommend that users migrate to this higher resolution model.
Blackout zones introduced in previous versions have been updated in WMM2025 to represent small changes in location. These zones near the north and south poles mark places where the Earth’s magnetic field may not be usable for navigation.

model cooperation
WMMs are essential for accurate navigation, and because the Earth’s magnetic field changes in unpredictable ways over time, especially over periods of several years or more, WMMs are updated at least every five years. Compasses are affected by the Earth’s magnetic field, so having the latest models will ensure your navigational instrument provides accurate readings.
WMM is a standard model used by the UK and US governments, including the US Federal Aviation Administration and the US Department of Defense, as well as international authorities such as the North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO). International Hydrographic Organization and British Hydrographic Office. Smartphone and consumer electronics companies also leverage WMM to provide consumers with accurate compass apps, maps, and GPS services.
WMM was jointly developed by NOAA’s National Center for Environmental Information (NCEI) and the British Geological Survey (BGS) and is a joint product of the US National Geospatial-Intelligence Agency (NGA) and the UK’s Defense Geographic Center (DGC). ). Models, related software, and documentation are distributed by NCEI on behalf of NGA and BGS on behalf of DGC.
NCEI and WMM
NCEI, with support from the Cooperative Research Institute for Environmental Sciences (CIRES), plays a key role in the development, maintenance, and distribution of WMM.
NCEI develops and distributes geomagnetic models and maintains an archive of geomagnetic data to improve the understanding of the Earth’s magnetic field and its dynamic changes. NCEI also provides tools and services to visualize, access, and utilize WMM and other geomagnetic data products and models.
NCEI works with partners to conduct research to better understand the Earth’s magnetic field, its variations, and its potential impacts on the Earth and its technologies. This research will help improve the accuracy of WMMs and contribute to the scientific community’s broader understanding of the Earth’s magnetic field and its various sources, from the core to near-Earth environment currents.
NCEI also participates in international efforts such as the International Geomagnetic and Aeronautical Association (IAGA) to ensure that WMM reflects a global and collaborative approach to understanding and predicting changes in the Earth’s magnetic field. .
See below for more information.