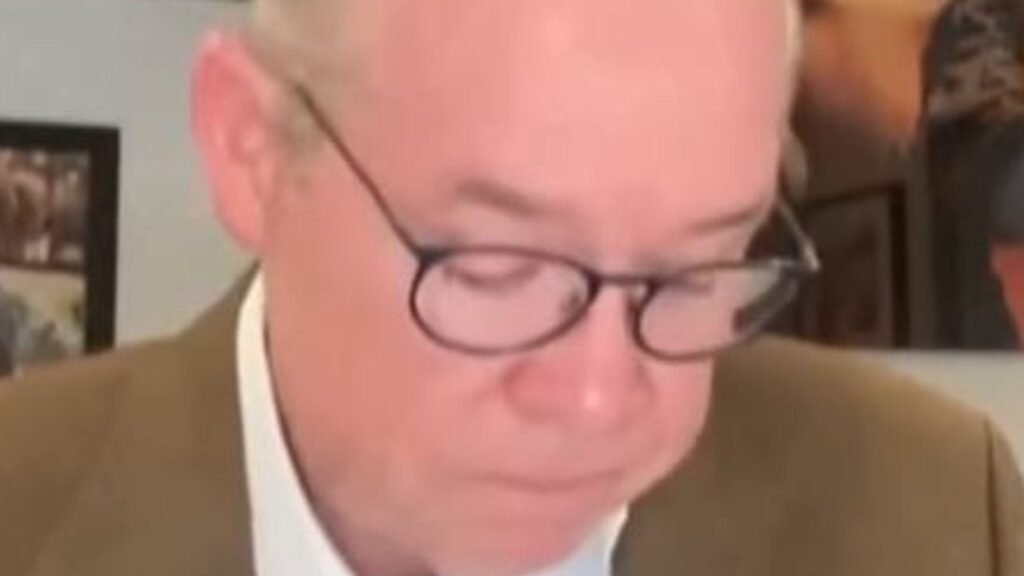
Hurricane Milton brought a US meteorologist with 33 years of hurricane experience to tears on live TV.
NBC’s John Morales later said it was atmospheric pressure that caused the moment.
“It’s funny how nerds lose millibars because of millibars,” he says.
A drop in air pressure is the best way to predict storm intensity.
Hurricane Milton updates – tourists stranded
Forecasters had just received an update from the National Weather Service revealing that Milton’s air pressure had dropped by 50 millibars in just 10 hours.
“It just fell like a rock,” Morales said.
He had never seen a hurricane strengthen so quickly from a tropical storm to a Category 5 hurricane in just one day.
But it also caused a flare-up and caused him to uncharacteristically lose his cool.
Sea surface temperatures in the Gulf of Mexico are currently about 2 to 3 degrees warmer than the 20th century average.
Warmer oceans make storms more active, and increased evaporation of water from warmer oceans adds more water to storms, producing more rain.
Morales blamed a growing “anxiety” over the fact that global warming is unchecked as part of what makes Milton so exceptional.
The hurricane weakened overnight but has now re-intensified, becoming a Category 5 storm. It is expected to weaken to a Category 3 storm just before making landfall in central Florida.
However, its highly unusual track and massive size make this storm the largest to hit this part of Florida in recorded storm history.
Read more on Sky News:
What we know about Hurricane Milton
Evacuation ahead of “worst storm of the century”
Another important factor is the fact that Milton will create a compound disaster that will blast the damage from Hurricane Helen, which left debris across the Florida peninsula.
They will weaponize debris, broken tree branches, collapsed buildings and trash cans to cause further damage.
There is uncertainty about how climate warming will affect the number of hurricanes that are likely to occur each year.
However, the relationship between global warming and the strength of future storms is now indisputable.